Ladle is one of the equipment required for steelmaking process. With the improvement of converter life, the increase of continuous casting ratio and the progress of refining technology outside the furnace, the ladle is in increasingly harsh conditions of use such as large capacity, multiple steel types, high temperature and long time, and the requirements for refractory materials for ladle are also constantly increasing.
In the past ten years, my country has learned from foreign experience and started to change refractory bricks to amorphous refractory materials, and built the whole lining by projection, ramming, pouring and other methods. The use of projection construction saves 50% of labor compared with bricklaying construction. The projection materials include high zircon, MgO-Al2O3, MgO-SiO2 and Al2O3-C.
Problems and countermeasures encountered in the development of refractory materials for domestic ladles at present.
1.The proportion of brickwork is high
At present, a considerable part of Baosteel’s ladles still use high-alumina bricks. Under the condition of equivalent cost, the refractory consumption of brick-built ladles per ton of steel is about 1kg higher than that of monolithic ladles. It is unwise to continue to use high-alumina bricks. Compared with monolithic casting ladles, brick-built ladles have the following shortcomings: first, the melting loss is fast and the pollution to molten steel is large; second, the masonry workload is large and maintenance is difficult; third, the safety is poor. Therefore, monolithic casting ladles should be used as soon as possible on ladles with conditions. The cladding of some 300t ladles has been used for a long time and has been severely deformed, and it is no longer possible to put it into the mold core for casting. Prefabricated bricks have also been tested for this part of the cladding. The cost and consumption are equivalent to or even better than the monolithic ladles. They are currently in use. It is necessary to further promote them after gaining experience.

2.Low life of the bottom of the bag
At present, Baosteel uses wax stone-silicon carbide bricks for the bottom of the ladle, which have a service life of only 25 times. This is the worst link in the refractory materials of the ladle and the main reason for the high consumption of refractory materials. Baosteel also uses integral casting of the bottom of the ladle on some ladles. The main reason why it cannot be used in large quantities is the difficulty in maintenance. Since the minor repair cycle is only 25 times, there are many cold steel interlayers after multiple repairs, and the service life cannot reach more than 125 times reported abroad. At the same time, the cost per ton of steel is also 2-3 times that of wax stone-silicon carbide bricks. Currently being tested is the use of aluminum-magnesium spinel prefabricated bricks in the impact zone and high-aluminum unfired bricks around, with a target service life of 50 times.
3.Minor repair cycle is too short
At present, the minor repair cycle of Baosteel’s ladle is 25 times, while the international advanced steel mills generally have about 50 times. The short minor repair cycle leads to high consumption of refractory materials and low thermal turnover rate of the ladle. The main obstacle to improving the minor repair cycle of the ladle is the low life of the upper nozzle and the air brick. Tests have been conducted on the upper nozzles of various materials, and it is difficult to significantly improve the life. A repair ring has been developed that can extend the life to more than 25 times. The structure of the upper nozzle and the seat brick is currently being studied to enable it to be replaced in a hot state, and it is estimated that it will be successful soon. Many ladles at home and abroad are implementing hot replacement of air bricks, and Baosteel also needs to solve this problem as soon as possible.
4.High consumption of refractory materials for special steel
Some steel grades (such as steel cord steel and electrical steel) have particularly large melting losses on refractory materials, especially steel cord steel, which has special requirements for refractory materials and cannot be used with general refractory materials. When smelting this kind of steel, the slag line life sometimes does not even reach 10 times, the number of ladle repairs is high, and the consumption of refractory materials is extremely high. Although the output of this kind of steel is not large, it has a great impact on the consumption of refractory materials in the ladle. It is necessary to develop refractory materials that meet the smelting requirements of these steel grades.
5.Maintenance judgment technology and standards are backward
To reduce the consumption of ladle refractory materials, there must be a scientific and reasonable residual thickness management standard. Since the residual thickness of the ladle is basically judged manually, it is arbitrary and risky. Operators often consider the importance of ladle safety production more and ignore the cost. To reduce the consumption of ladle refractory materials, there must be advanced judgment and maintenance technology, such as: using laser thickness measurement to ensure the safe use of the ladle; using wet spraying technology to maintain the ladle lining; air brick hot replacement safety system. By improving the reliability of the safe use of refractory materials, the waste of refractory materials can be reduced.
Looking at the development and current status of refractory materials, it can be considered that the future development trend of ladle refractory materials is:
(1) Focus on the development and utilization of local resources, especially make full use of waste resources. Develop neutral and alkaline refractory materials.
(2) The life of domestic ladles is relatively low, so alkaline linings, spinel linings, high-aluminum linings and their corresponding composite lining structures will appear in large quantities.
(3) The proportion of domestic amorphous refractory materials used in ladles will continue to increase, which is of great benefit to small die-casting manufacturers, but for manufacturers using continuous casting technology, high-quality composite brick ladles will account for a considerable proportion.
(4) The application scope of carbon-containing products continues to expand.
(5) Reduce consumption and clean ladles. Reducing consumption can not only reduce costs, but more importantly, it can reduce pollution to molten steel; cleaning ladles requires the use of carbon-free and low-melting-loss refractory materials on the one hand, and reducing slag sticking to the ladles on the other hand.
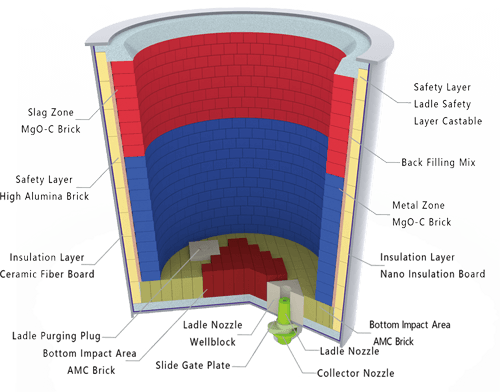
More details about Ladle Refractorie:
What is ladle refractory?
In the realm of refractories, the ladle is a term used for a vessel that is capable of withstanding extremely high temperatures of molten metals. This vessel is the primary medium to carry and transport these molten materials. As for the size of a ladle, it can hugely vary as per the requirement.
What does refractory mean in pottery?
Refractories are ceramic materials designed to withstand the very high temperatures (in excess of 1,000°F [538°C]) encountered in modern manufacturing. More heat-resistant than metals, they are used to line the hot surfaces found inside many industrial processes.
What is the refractory used in ladle furnace?
RG30-DOL is a premium quality refractory for more aggressive wear areas in slag lines and impact pads of ladle furnaces. High purity sintered dolomite that is sized, blended with magnesite, a resin and carbon system, pressed and heated to remove volatiles and create good ambient temperature strength.
What materials are used in ladles?
In modern times ladles are usually made of the same stainless steel alloys as other kitchen utensils; however, they can be made of aluminium, silver, plastics, melamine resin, wood, bamboo or other materials.
What are molten steel ladles made of?
They are steel fabricated shells that are lined with refractory to insulate them from the heat and to hold the temperature of the metal.
